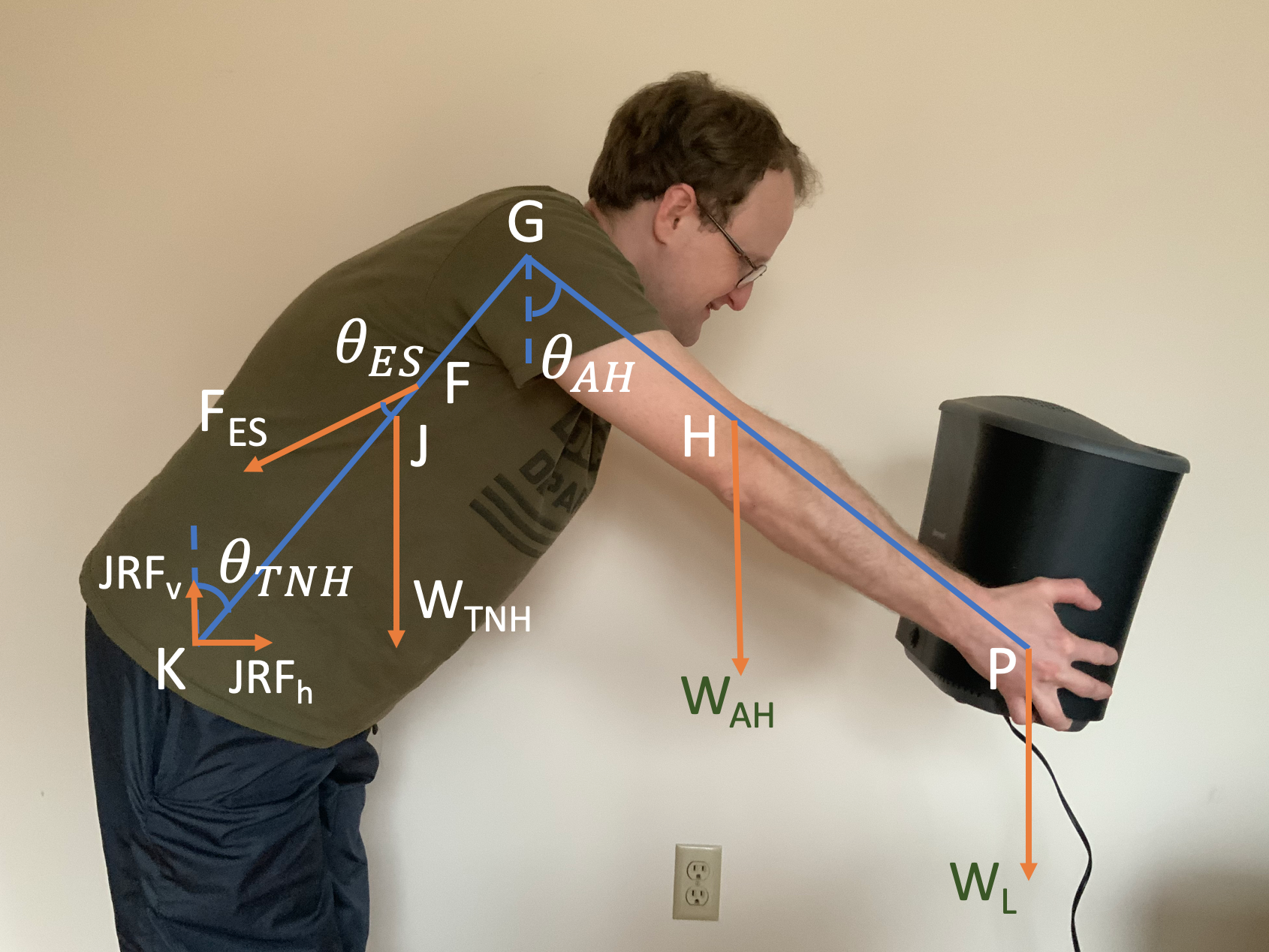
Simulation of Back and Arms II
Objectives: 1. Find the optimal posture for lifting a load. 2. Apply the conditions of equilibrium to determine the amount of force that is exerted by the person’s Erector Spinae muscle FES when the person is bending over to support a load. 3. Calculate the magnitude of the Joint Reaction Force JRF. 4. Find out how the force on the person’s erector spinae muscle and the joint reaction force depend on postures.